본 내용을 들어가기 전에 자바스크립트의 fetch()에 대해 간략히 알아보겠습니다.
0️⃣ fetch()
fetch()는 필요할 때 서버에 네트워크 요청을 보내고 데이터를 받아오는 일을 하는 메서드입니다.
let getUser = fetch('https://example/api...')
.then((response) => response.json())
.then((json) => json.userInfo[0])
.then((user) => console.log(user.name))해당 메서드를 호출하면 요청을 보낸 뒤 Promise가 Response의 인스턴스와 함께 '이행' 상태가 됩니다.
그렇게 전달받은 객체는 then() 메서드를 통해서 다룰 수 있습니다.
하지만 이렇게 then() 메서드를 계속 붙여서 사용하다보니 가독성이 떨어지고 유지보수가 어려워지는 상황이 발생할 수 있습니다. 이를 해결하고자 async와 await이 등장하게 되었습니다.
1️⃣ Promise
자바스크립트의 Promise 객체는 비동기 작업의 완료 또는 실패 결과를 제공하는 객체입니다.
let promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {})이런식으로 객체를 생성할 수 있습니다!
여기서 resolve와 reject는 자바스크립트에서 자체적으로 제공하는 콜백으로, 각각 '성공'과 '실패'시에 호출됩니다.
resolve: 작업이 성공적으로 끝난 경우 그 결과를 나타내는 value와 함께 호출reject: 실패(에러)시 에러 객체를 나타내는error와 함께 호출
이렇게 생성된 promise는 state와 result 라는 내부 프로퍼티를 갖게 되고, 비동기 작업을 완료한 후 resolve나 reject를 호출하게 되면 promise 객체의 상태가 변화하게 됩니다.
| state | result | |
|---|---|---|
| 생성 | "pending" | undefined |
| resolve | "fulfilled" | value |
| reject | "rejected" | error |
이렇게 promise는 resolve와 reject중 하나를 호출하며, 상태가 변경되면 더 이상 상태는 변하지 않게 됩니다.
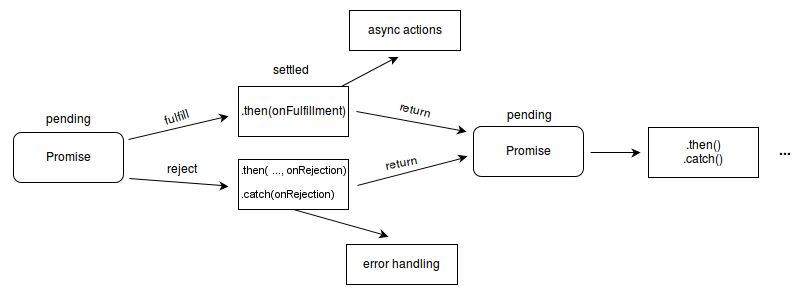 이미지 출처: MDN - promise
이미지 출처: MDN - promise
2️⃣ Promise Chaining
앞에서 fetch를 알아볼 때 코드에서 then() 메서드를 계속 이어붙여서 처리하는 모습을 보였습니다. 이를 Promise Chaining이라고 합니다.
then()은 결과로 Promise 객체를 반환하기 때문에 연쇄적으로 사용할 수 있는 것입니다.
let getUser = fetch('https://example/api...')
.then((response) => response.json())
.then((json) => json.userInfo[0])
.then((user) => console.log(user.name))Promise Chaining이 없었을 당시에 여러 비동기 작업을 연속으로 수행할 경우 함수의 매개변수로 콜백 함수를 계속해서 반환하는 '콜백 지옥'이 나타났었습니다.
3️⃣ Promise catch
Promise의 state가 'rejected' 상태가 되어 error를 반환한다면 이를 처리해줄 요소가 필요한데, 이를 Promise의 catch() 메서드를 이용하여 처리할 수 있습니다.
let getUser = fetch('https://example/api...')
.then((response) => response.json())
.then((json) => json.userInfo[0])
.then((user) => console.log(user.name))
.catch((error) => console.log(error))catch() 메서드도 then() 메서드와 마찬가지로 Promise를 반환하기 때문에 then()처럼 Promise Chaining이 가능합니다.
let getUser = fetch('https://example/api...')
.then((response) => response.json())
.then((json) => json.userInfo[0])
.then((user) => console.log(user.name))
.catch((error) => console.log(error))
.then(() => console.log('에러 처리 이후 수행'))또한 catch() 메서드는 Promise가 '이행'되었다면 호출되지 않으며, resolve가 호출된 이후에 발생한 오류는 무시하게 됩니다.
4️⃣ Promise finally
try ~ catch ~ finally 문법 처럼 Promise도 작업이 '이행'되거나 '거부'된 이후에 호출할 함수를 finally() 메서드로 예약할 수 있습니다.
let getUser = fetch('https://example/api...')
.then((response) => response.json())
.then((json) => json.userInfo[0])
.then((user) => console.log(user.name))
.catch((error) => console.log(error))
.finally(() => console.log('유저 정보 받아오기 종료'))5️⃣ Promise 동시성
Promise는 작업의 동시성을 용이하게 하기 위해 여러 메소드를 제공합니다.
Primise.all() 메서드는 순회가 가능한 객체를 매개변수로 받습니다. 이 객체에는 Promise가 들어있어야 합니다.
Promise.all([promise1, promise2, promise3])각각의 Promise들이 모두 '이행' 상태가 된다면 결과를 담고있는 객체를 반환합니다. 하지만 하나라도 '거부' 상태가 된다면 Promise.all도 '거부' 상태가 됩니다.
Promise.all([promise1: resolve, promise2: reject, promise3]) // '거부'반대로 Promise.all 과 다르게 하나만 '이행' 상태가 되어도 그 이행 값을 반환하는 메서드인 Promise.any()가 있습니다.
Promise.any([promise1, promise2, promise3])Primise.any는 '거부' 상태가 되더라도 그 다음으로 '이행' 상태가 되는 promise의 값을 반환합니다.
// promise3의 이행된 값을 반환한다.
Promise.any([promise1: reject, promise2, promise3: resolve])또한 가장 먼저 완료된 값의 결과를 그대로 반환하는 Promise.race(),
주어진 모든 Promise의 결과를 나타내는 객체 배열을 반환하는 Promise.settled() 메서드도 있습니다.